T2T Specification: A Revolutionary Material in OLED Technology
The field of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) is in a constant state of evolution. Amidst a sea of materials and compounds that are pushing this technology to new heights, T2T emerges as a promising element in the OLED stack.
Understanding T2T
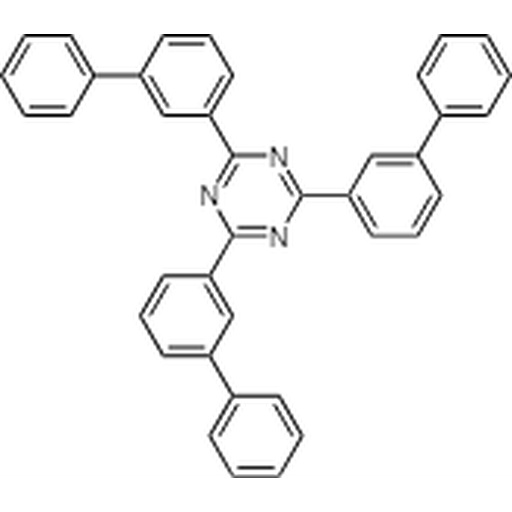
T2T, fully known as 2,4,6-Tris(biphenyl-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine, is a highly efficient electron transport material. Its unique structure, characterized by a triazine core and three biphenyl groups, makes it an invaluable asset in organic electronic devices.
Key Features of T2T
- Electron Transport Layer (ETL) Material: T2T’s electron-deficient nature makes it an ideal candidate for use in electron transport layers. This systematic approach promotes OLEDs to function efficiently and extends their lifetimes.
- TADF Material: One of the advanced features of T2T is its ability to be used in Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence (TADF) OLEDs. This property is crucial for the development of next-generation OLEDs.
- Host Material for PHOLEDs: T2T has proven its worth as a host material in Phosphorescent Organic Light Emitting Diodes (PHOLEDs), offering enhanced emission and energy efficiency. This host material demonstrates sufficiently high triplet energies and favorable electron transfer properties, making it a suitable choice for accommodating green phosphorescent emitters. This enables the creation of highly efficient PhOLEDs with low-driving voltage requirements
The Role of T2T in Modern OLEDs
In the modern OLEDs world, there is an intense demand for materials that offer high efficiency, durability, and low energy consumption. T2T, with its unique attributes, fits this requirement perfectly. Its role as an ETL material ensures that OLEDs are not only efficient but also have longer lifetimes.
Conclusion
The OLED industry is continuously expanding and the need for materials that are both efficient and long-lasting is more pressing than ever. T2T, with its unique properties and proven performance, is poised to play a significant role in the future of OLED technology. As scientific research progresses and technology advances, it’s clear that T2T will find increasingly diverse applications in organic electronic devices.