Sublimation
Our approach to sublimation
At Noctiluca, we specialize in advanced sublimation services. With the state-of-the-art equipment and expertise we ensure the highest levels of purity and quality in the final product.
Noctiluca provides the expertise and resources to streamline your sublimation process effectively. How the process of the sublimation service looks like? See the detailed guideline below.
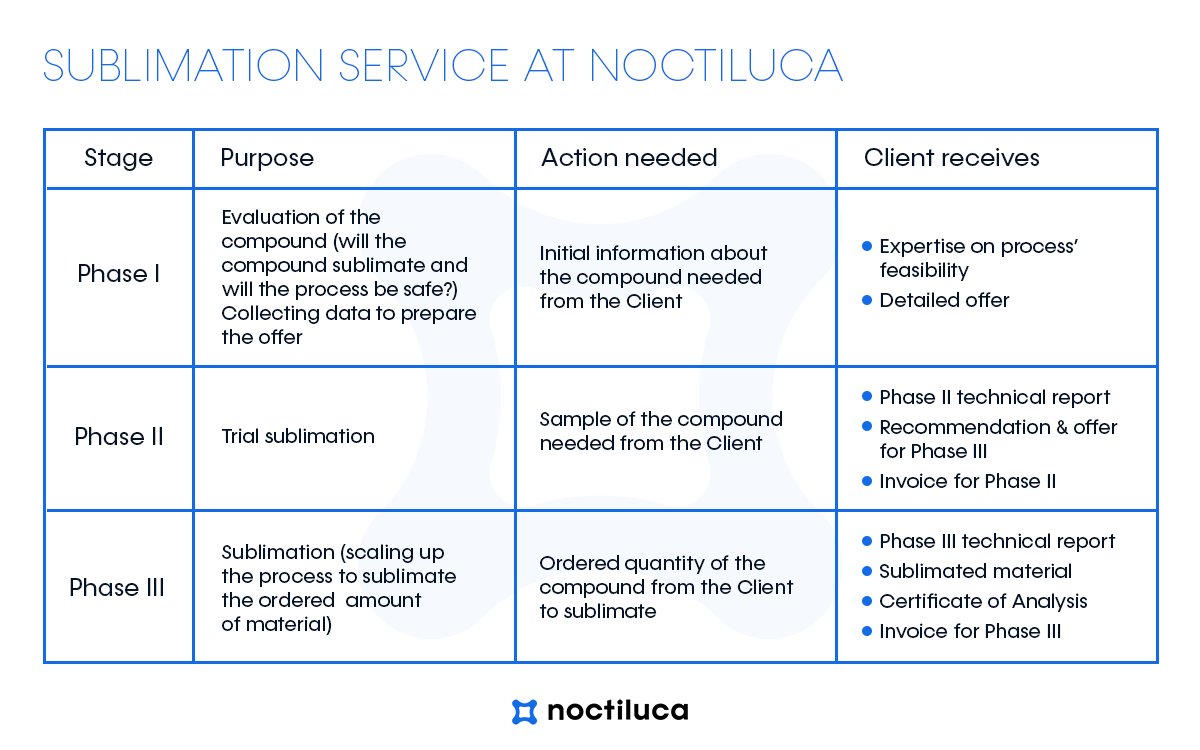
STAGE I – INITIAL QUESTIONS
To ensure we deliver the most effective sublimation service to our customers, we kindly request detailed information about the product slated for the sublimation process. If certain details are unknown or confidential, please notify us, and we’ll strive to assist you nonetheless. Obtaining a comprehensive understanding at the outset will streamline initial communication and enable us to furnish you with a tailored offer. The overall cost of sublimation is contingent upon numerous factors and varies significantly for each compound. Therefore, there isn’t a “fixed” price we can provide at this stage. For further insights, please go to our FAQs section below.
Download the Questionnaire Form with initial inquiriesWhat is happening in this stage?
Upon receipt of your sublimation inquiry, we will proceed by either sending you a list of supplementary questions or our team will commence analyzing the provided information to assess the feasibility of sublimating your compound. This process typically requires a few days to complete.
What does the customer get at the end of this stage?
We will offer our assessment regarding the feasibility of sublimating a specific compound. Additionally, you will receive a detailed outline of the sublimation process that we can provide, segmented into stages. Finally, you will be presented with a commercial offer for the subsequent stage.
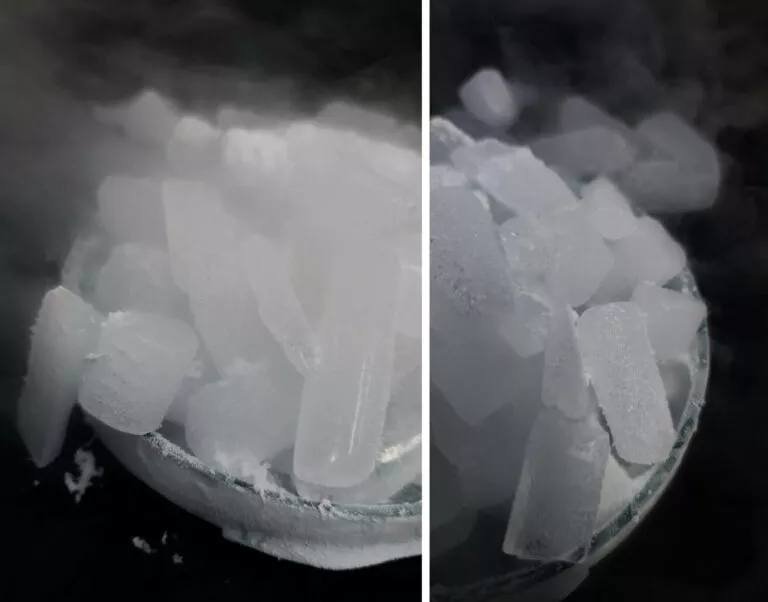

STAGE II – TRIAL SUBLIMATION
What is the reason for this stage?
The outcome of the sublimation process is contingent upon numerous factors, making it challenging to predict solely based on available information. Hence, it’s essential to assess how a specific compound will undergo the sublimation process in our sublimator. Conducting several tests enables us to determine the optimal process parameters, streamline timing, and provide a comprehensive offer for sublimating the entire material quantity.
What is happening in this stage
During this phase we will request the delivery of a sample of the material for sublimation, typically around 3-5g. Subsequently, we will conduct analytical tests to determine the material’s purity and thermal properties. We will then commence trials of the sublimation process, analyzing the purity of the resulting product and its yield after each trial. Ultimately, we will compile a technical report summarizing the trials and provide a commercial offer for sublimating the entire material quantity. We anticipate that this stage will likely span approximately 2-3 weeks from the receipt of the material for trials.
What does the customer get at the end of this stage?
As a culmination of this stage, you will receive a comprehensive technical report detailing the analyses conducted, sublimation yield achieved, purity levels attained, and the process parameters employed. Based on these trials, we will ascertain whether the material successfully undergoes the sublimation process and propose optimized process parameters for the remaining quantity of material, ensuring effective sublimation yield. Also you will receive our offer for sublimating the remaining amount of material and the invoice for the test phase.

STAGE III – SUBLIMATION
What is the reason for this stage?
In essence, our goal is to sublime the material and deliver to our customer a fully processed product with confirmed purity.
What is happening at this stage?
Upon receiving the material for sublimation, our team will initiate the scaling-up process based on the initial sublimation trials. We will strategize the number of batches and sublimation runs required and carry out the sublimation process accordingly. Prior to and following the process, we will conduct purity analyses of the material. Ultimately, we will consolidate all results into a comprehensive technical report and deliver the processed product to our customer.
What does the customer get at the end of this stage?
We will deliver your sublimated product along with the technical report from this phase, detailing the process parameters. Additionally, you will receive a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) confirming the final product purity. At this stage, you will also receive the final invoice for the sublimation service.
Check General Contractual Terms and Conditions and Information for Customers
Sublimation Explained
Sublimation is an endothermic process where a substance transitions directly from the solid phase to the gas phase, bypassing the liquid state. This transition occurs under specific temperature and pressure conditions, below the substance’s triple point on its phase diagram. The triple point is the threshold pressure where the substance can exist in its liquid form.
While most chemical compounds and elements exhibit three states at various temperatures under typical pressures, the transition from solid to gas often involves an intermediate liquid phase. It’s essential to note that the “pressure” in this context pertains to the substance’s partial pressure and not the system’s overall pressure. If a solid’s vapor pressure exceeds the surrounding partial pressure, it can sublimate, with some substances showing a higher inclination towards sublimation than evaporation. This inclination often arises from their elevated triple point pressures, making it challenging to obtain them in a liquid state.
The Utility of Sublimation in Chemistry
Sublimation serves as a critical technique for chemists, especially for compound purification. It’s a more efficient alternative to the time-consuming crystallization process, enabling the purification of even minuscule substance amounts. During sublimation, a solid is placed in a specialized apparatus, heated under vacuum conditions. As the pressure reduces, the solid volatilizes and condenses as a purified compound on a cooled surface, the “cold finger”, leaving non-volatile impurities behind. Once heating ceases, the purified compound can be retrieved from this cooled surface.
To maximize purification efficiency, a temperature gradient is employed. This strategy enables separating different compound fractions. Vacuum tube sublimation instruments aim to purify organic mixtures under vacuum conditions, essentially recrystallizing after evaporation. A controlled heating mechanism in an evacuated glass tube allows for distinct re-condensation points, depending on compound volatilities.
Heat absorption during sublimation facilitates the molecular transition into the vapor phase, categorizing it as an endothermic process. The heat of sublimation can be determined by summing the heat of fusion (solid to liquid) and the heat of vaporization (liquid to gas).

Problems addressed and applicability
Sublimation, particularly vacuum sublimation, is pivotal for purifying organic compounds in industries requiring purities often above 99%. This high purity is essential for consumer electronics, organic optoelectronic materials, and nanomaterial applications. Sublimation not only eliminates impurities but also volatiles, which can hinder high-temperature manufacturing processes.
Who benefits?
- Next-Generation Tech Materials: Sublimation is integral to developing materials for cutting-edge technologies. It ensures top-tier purity, promoting the efficiency of end-use applications in devices like mobiles, monitors, and solar cells.
- Academic and Industrial Synergy: Leading universities and research labs leverage sublimation services for material purification, fostering a smooth transition from discovery to practical application in advanced tech sectors.
- OLED Tech: Organic electronic technology advancements necessitate compounds with purity levels exceeding 99%. Sublimation ensures this high purity, enabling innovations like flexible OLED displays.
- Perovskite Solar Cells: In producing high-quality perovskite materials for solar cells, sublimation is crucial to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Our sublimation services exclude drug, intermediate product, and active pharmaceutical ingredient manufacturing due to the lack of cleanroom facilities. However, if sterility isn’t mandated, we’re open to discussions about purification via sublimation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is sublimation?
Where to start and what information we will require at the beginning?
How much does the sublimation cost?
Recognizing this, we’ve structured the valuation into stages. Upon receiving responses to the initial questions in our questionnaire you’ll receive a proposal for the test phase. Following the test phase, we’ll provide a separate offer for the main phase. This ensures transparency regarding costs at each stage of the process.
What will be the final purity of sublimed compounds?
What does the sublimation efficiency is?
Purity of the starting material: sublimation works best when the starting material is relatively pure. Contaminants or impurities may not sublimate at the same temperature as the desired compound, leading to incomplete purification.
Temperature control: sublimation typically occurs at specific temperature and pressure conditions. Controlling these parameters precisely ensures that the desired compound sublimates while minimizing the sublimation of impurities.
Pressure control: in some cases, adjusting the pressure can improve the efficiency of sublimation. Lowering the pressure can facilitate the sublimation process by reducing the boiling point of the substance.
Surface area: increasing the surface area of the substance can enhance sublimation efficiency. This can be achieved by grinding the material into a fine powder or optimization of material quantity and it’s distribution before sublimation process.
Residence time: allowing sufficient time for the sublimation process to occur can improve purification efficiency. However, excessively long residence times may lead to degradation or decomposition of the substance.
Collection and separation techniques: proper collection and separation of the sublimed material from any remaining solid impurities are crucial for achieving high purity.
Overall, the efficiency of sublimation in material purification depends on a combination of these factors, and optimizing each aspect can lead to higher purity and yield of the desired substance. However, based on our experience we are predicting a 50% yield of the sublimation process. In case of better efficiency every gram of sublimed material above the 50% yield will be delivered to you free of charge.
How much time is required for the sublimation?
What compounds are not suitable for the sublimation process?
Highly reactive compounds: Compounds that are highly reactive or prone to decomposition under elevated temperatures may not be suitable for sublimation. Sublimation typically involves heating the compound to relatively high temperatures, which could lead to degradation or chemical reactions.
Compounds with low volatility: Sublimation requires the compound to have sufficient vapor pressure at the sublimation temperature to transition directly from a solid to a gas phase. Compounds with low volatility may not readily vaporize at the temperatures and pressures used for sublimation.
Compounds with high melting points: Sublimation is more efficient for compounds with moderate to low melting points. Compounds with extremely high melting points may require impractical temperatures and pressures to sublimate effectively.
Ionic compounds: Ionic compounds, such as salts, may not sublimate easily because of the strong electrostatic interactions between ions in the solid state. Sublimation of such compounds may require extreme conditions that could lead to decomposition or dissociation of the ions.
Large organic molecules: Large organic molecules, such as polymers or complex biomolecules, may not undergo sublimation efficiently due to their size and complexity. Sublimation typically works best for smaller organic molecules with simpler structures.
Compounds with significant hydration or solvent molecules: Compounds that contain significant amounts of water or solvent molecules in their crystal structure may not sublimate cleanly. Instead of subliming directly, they may undergo partial melting or solvent evaporation, leading to incomplete purification.
Compounds that can react with materials like stainless steel or quartz: these are the materials from which the sublimator is made and the use of interacting compounds would cause permanent damage to the instrument.
These are just a few examples, and the suitability of a compound for sublimation depends on its specific properties and the conditions used for the sublimation process. This is also a reason why we ask so many questions at the very beginning.
